PREMISE
Reducing Dutch households’ electricity consumption using a chatbot with a recommender system that provides personalized usage tips based on their usage pattern.
SYNOPSIS
This study aims to develop a chatbot with a recommender system back-end that can help households reduce their electricity consumption by offering usage patterns and recommending energy-efficient alternatives. The chatbot can also provide real-time usage data, alerts, and energy efficiency tips for devices. The study’s main goal is to assess the chatbot’s effectiveness in promoting energy efficiency among homeowners (for households that have migrated to the Netherlands within the past five years).
SCOPE OF THE RESEARCH AND LITERATURE INSIGHTS
The study emphasizes the importance of reducing energy consumption in households. The COVID-19 pandemic and Russia’s manipulation of EU energy markets have compounded the energy crisis in the region, making it imperative to explore innovative solutions to address the situation (Agnieszka, 2022).
The present era has witnessed a proliferation of several applications and devices designed to aid homeowners in monitoring and tracking their electricity usage. These include digital meters, smart electrical outlets, and electricity tracker applications (Gielen, 2019). Digital meters offer the advantage of real-time tracking of energy consumption, which enables consumers to identify areas with high energy usage and make necessary adjustments to minimize consumption. Similarly, smart electrical outlets allow users to remotely turn off devices and appliances that are not in use, thus reducing unnecessary electricity consumption. Moreover, electricity tracker applications provide consumers with detailed information regarding their energy usage patterns, allowing them to make informed decisions about their energy usage habits. Employing these technologies can result in not only a reduction in electricity bills but also a decrease in the carbon footprint and promotion of sustainable living (Brown, 2019). Digital electrical meters have been widely adopted in the EU to enhance the energy efficiency, enabling consumers to monitor and adjust their usage patterns accordingly.
In addition to digital meters, chatbots have emerged as a promising technology for promoting energy efficiency. Chatbots have a wide range of applications, including education, business, and information retrieval. In the context of energy consumption, a chatbot app can read energy consumption from meters and report it to energy suppliers, providing guidelines on how to optimize energy use (Rocha et al., 2021).
How does this study differ from previous research attempts?
This research sets itself apart from previous studies by concentrating on developing a unique application that takes advantage of chatbots’ capabilities to give users personalized insights into their electricity usage. Although other tools and devices exist for monitoring energy consumption, they primarily provide users with information on real-time usage or historical trends, The previous systems were observed to lack any provision of suggestions or recommendations for the efficient utilization of electricity for electronic devices. In contrast, the proposed chatbot app aims to provide users with recommendations on optimizing their energy consumption by offering insights on how frequently to use specific electrical devices to prevent excessive consumption.
First iteration
In this research, the primary objective is to develop an efficient and user-friendly chatbot interface for a recommender system that can satisfy the needs of its users. One of the challenges in designing a chatbot interface for a recommender system is that users cannot see the system’s recommendation process, which may lead to confusion and dissatisfaction. Therefore, the focus of this study is on developing a chatbot interface that can effectively communicate with users. To enhance the comprehension of designing a chatbot for user interface, this study attempts to experience several tools used for developing a chatbot. The tools evaluated in this study include VoiceFlow, Dialogflow, Landbot, and Python coding. Ultimately, the study selected VoiceFlow for creating a textual chatbot and utilized Python coding for developing a voice-recommend chatbot. The rationale behind choosing these tools was due to their simplicity and ease of use.
The first step was to identify the most suitable type of chatbot interface (Journal I. R. J. E. T., 2022), considering the pros and cons of chatbots with voice commands versus chatbots with text and button commands (Huang and CIS, 2021). To this end, two different chatbot designs were presented to a group of five users, and their feedback was analyzed.
The results revealed that three out of five users preferred the chatbot with text and button commands. The users mentioned that it was easier for them to use the chatbot and also because they have some pronouncing problems that could cause wrong commands in the chatbot because the chatbot is using pre-made libraries such as ‘SpeechRecognition’ in python. The chatbot with text and button commands was deemed the most suitable option for this study.

Image of the Chatbot written in Python
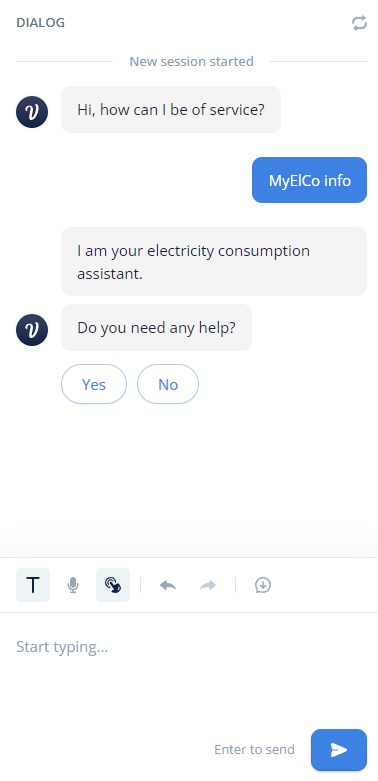
Picture of textual chatbot made via VoiceFlow
second iteration
The present study represents the second iteration that sought to identify the most pressing concerns and information needs of users while interacting with an energy usage monitoring and management application. The study was designed to gain a deeper understanding of users’ needs and preferences and to provide insights for the app on how to improve the app’s user experience.
To achieve the study’s goals, a premade sheet was created that users could fill out with their questions and information needs about their electricity usage. The survey data collected from the participants were then analyzed to identify the most frequently asked questions and information requirements.
The results of the survey revealed that users were particularly interested in knowing about their real-time electricity usage, as well as general tips on how to use their electrical devices more efficiently. Moreover, users expressed interest in having access to information about their list of electrical devices and patterns that could help them to reduce their electricity bills by using their devices more efficiently.
These findings underscore the importance of understanding users’ needs and preferences when designing apps for energy usage monitoring and management. By providing users with relevant and timely information, the app can help users make informed decisions about their energy usage.
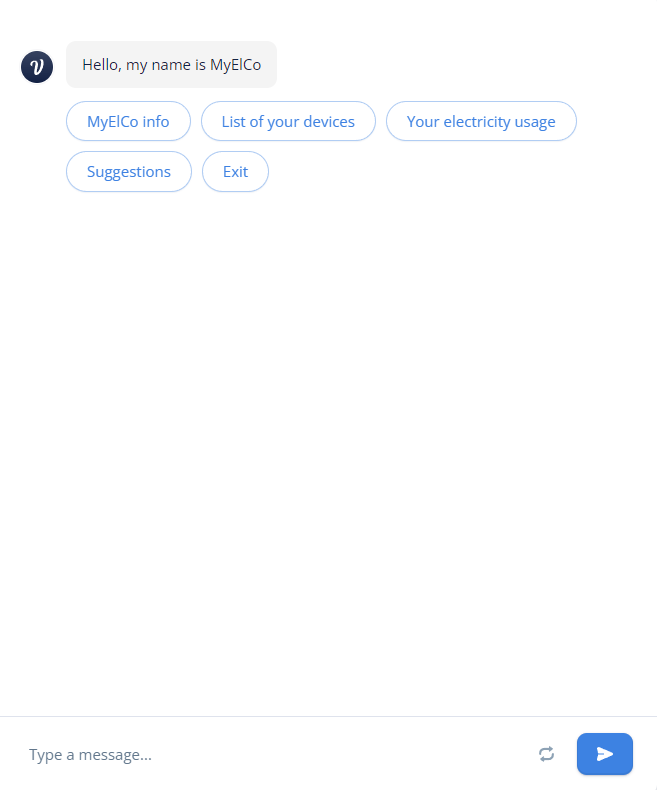
third iteration:
During the user testing phase, the application was distributed to users to ensure that feedback was received from a range of individuals. The user trials were conducted over time and participants were encouraged to provide detailed feedback on any aspect of the application that required improvement.
One of the primary issues that emerged from the user trials was the need for more intuitive user interfaces. Participants reported that while they found the chatbot to be a useful feature, they often struggled to understand how to use it effectively. To address this issue, a new design introduced pre-made buttons.
Another important issue is that users reported experiencing issues with the chatbot when they attempted to enter commands that deviated from the expected sequence. For example, if a user attempted to inquire about their device usage while in the middle of receiving information about their device list, the chatbot would often fail to provide an accurate response. To address this issue, a new design was implemented to create new intents during the application design process that enabled the chatbot to recognize and respond to a wider range of user queries.
CONCLUSION
Reducing energy consumption is a critical issue, particularly within the European context, and various measures have been taken to address this challenge. One of the latest technologies that can be utilized to achieve this goal is Chatbot. In the context of energy consumption, a Chatbot app can be used to read energy consumption from meters manually and report it to households.
To accomplish the main goal of the study, the study conducted a thorough analysis of various chatbot design strategies and evaluated their efficacy in promoting energy efficiency among users. This study considered two different types of chatbots, including textual, and voice-based ultimately concluded that a textual chatbot would be most suitable for this particular application.
The next step in the study involved identifying the most common questions and information that users might need when using the energy conservation app. To reach this goal, several surveys and user interviews were conducted to gather data on user needs and preferences. Based on this information, the design of the chatbot provides personalized recommendations on how users can optimize their energy consumption, including tips on when to use specific electrical devices to avoid excessive consumption.
The third iteration was to evaluate the user interaction with the chatbot to identify any missed features or errors in the system and to observe and analyze the chatbot’s conversation with users to ensure that the app was meeting user needs.
Future research
The Chatbot designed for this study will have a recommender system back-end that will provide personalized recommendations to homeowners on how to optimize their use of electrical energy. The system will be trained on energy usage patterns, customer preferences, and other relevant data to generate tailored recommendations for each user.
The Chatbot will be integrated with other applications and services, such as digital electrical meters, to provide a more seamless user experience. It will also be able to collect and analyze data from various sources, such as user feedback and energy usage patterns, to continually improve its recommendations and user engagement.
References
Agnieszka, W. I. D. U. T. O. (2022). Energy saving and demand reduction.
Brown, M. A., & Zhou, S. (2019). Smart‐grid policies: an international review. Advances in Energy Systems: The Large‐scale Renewable Energy Integration Challenge, 127-147.
Energiewende, A. (2019). European Energy Transition 2030: The Big Picture IMPULSE.
Huang, X., & CIS, A. (2021). CHATBOT: DESIGN, ARCHITECTURE, AND APPLICATIONS.
Journal, I. R. J. E. T. (2022). Survey on Chatbot Classification and Technologies. IRJET.
Rocha, C. V., Vieira, P. H., Pinto, A. M., Bernhard, P. V., Junior, R. J. A., Marques, R. C., … & Monteiro, E. M. (2021, October). A comparative study of methods based on deep neural networks for self-reading of energy consumption in a chatbot application context. In Anais Estendidos do XXXIV Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (pp. 233-239). SBC.


